Hazard Analysis Critical Control Point (HACCP) is a systematic approach to ensuring food safety and preventing foodborne illness throughout the food production process. HACCP is widely implemented and internationally recognised in the food and beverage industry, including in Canada.
According to the Canadian Food Inspection Agency (CFIA), "HACCP is mandatory for all federally registered meat establishments and is becoming more widely adopted in other sectors of the food industry." However, many food and beverage industry professionals in Canada struggle with determining Critical Control Points (CCPs) and their critical limits, which are essential components of a successful HACCP plan.
Nowadays, digital solutions such as Software as a Service (SaaS) and Internet of Things (IoT) can help streamline the HACCP process and improve food safety. By leveraging these technologies, food and beverage industry professionals can automate data collection, analysis, and reporting, which can save time and resources while increasing the accuracy and effectiveness of their HACCP plans.
HACCP : from NASA to the food Industry
HACCP is a systematic and science-based approach that identifies and prevents potential food safety hazards in the food production process. The HACCP plan is a preventive tool that aims to ensure the safety of food products by breaking down the process into 12 steps, which are further categorized into 5 preliminary steps and 7 principles.
The HACCP plan was first developed in the 1960s in the United States, during the time when NASA and the army were planning to send humans into space. To ensure the safety of the food that astronauts were going to consume, the Pillsbury company was tasked with developing a tool that would avoid the systematic use of destructive controls. The HACCP plan was the result of this effort and was soon adopted by the food industry to prevent foodborne illnesses.
What are CCPs and Critical Limits, and why are they paramount?
According to the Safe Food for Canadians Regulations (SFCR), a CCP is defined as "a step at which the application of a control measure is essential to prevent or eliminate any biological, chemical or physical hazard that presents a risk of contamination of a food or to reduce the hazard to an acceptable level." Essentially, a CCP is a point in the food production process where a hazard can be controlled or prevented. The goal of identifying CCPs is to ensure that food products are safe for consumption and meet regulatory requirements.
Critical limits refers to the maximum or minimum set values that control a hazard at a critical control point (SFCR). They are established based on scientific data, regulatory requirements, and industry best practices. For example, critical limits for temperature may be based on the optimal temperature range for the growth of bacteria, while critical limits for pH may be based on the acidity level required to prevent the growth of pathogens. The goal of establishing critical limits is to ensure that hazards are controlled or prevented at each CCP, which ultimately helps to ensure the safety of the final food product.
Discover the Best Apps for Food & Beverage
Determining CCPs and their Critical Limits in 4 steps
To improve the identification of CCPs, organizations can use the four principles of Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points, which are 1, 2, 3 and 4 of the HACCP approach.
Principle 1: Conduct a hazard analysis
This step is conducting a hazard analysis, which involves identifying and evaluating potential hazards that may occur during the food production process. This step helps to identify potential hazards that can be controlled or prevented through the HACCP process.
Principle 2: Determine the critical control points (CCPs)
Once the hazards are identified, the next step is to identify potential CCPs in the food production process. CCPs are the points in the process where hazards can be controlled or prevented. For example, in the meat industry, a CCP may be the cooking process to ensure that the meat reaches the appropriate internal temperature to kill harmful bacteria.
Principle 3: Establish critical limits
After identifying CCPs, the next step is to establish critical limits. Critical limits are the boundaries that must be maintained to prevent, eliminate or reduce hazards to an acceptable level. They should be specific and measurable. If we take the previous example, a critical limit for the cooking process in the meat industry could be the minimum internal temperature that the meat needs to reach to ensure that harmful bacteria are eliminated. For instance, for ground beef, the recommended internal temperature is 71°C (160°F) to kill harmful bacteria such as E. coli and Salmonella. If the temperature of the meat does not reach this critical limit, it could pose a risk to consumers and must be either recooked or discarded. The establishment of critical limits must be based on scientific data and regulatory requirements.
Principle 4: Establish monitoring procedures (measuring CCPs)
This step is monitoring and measuring CCPs to ensure that critical limits are being met. This can be done through physical or chemical tests, or by using digital solutions such as IoT sensors or HACCP software. If critical limits are not being met, corrective actions must be taken to prevent the food product from being released into the market.
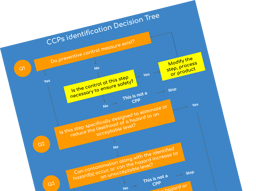
Recommended for you. Download our free "CCPs identification decision tree"
The role of digital Solutions for Streamlining HACCP approach
Digital solutions such as Software as a Service (SaaS) and Internet of Things (IoT) have revolutionized the way food and beverage industries approach food safety. By integrating digital solutions into the HACCP process, companies can enhance their risk management, save time, and reduce costs associated with food recalls.
Let’s see what are the most relevant ones:
HACCP planning and management software: SaaS based software software that allows the creation and management of HACCP plans and records. These solutions provide users with an easy-to-use, cloud-based platform that simplifies the development, implementation, and maintenance of HACCP plans. Companies can ensure that all regulatory requirements are met and data is accessible and up-to-date.
Real-time analytics and reporting tools: Another SaaS based software that allows companies to analyze data in real-time, providing actionable insights to improve food safety. By using these tools, companies can quickly identify and address any issues that may arise in the production process.
Traceability and recall management software: enable companies to track products throughout the supply chain and quickly initiate recalls if necessary. Provide companies with real-time data on a product's location, production date, and other relevant information, allowing them to quickly identify and address issues that may arise during the production or distribution process.
Compliance management: Cloud-based compliance management solutions simplify compliance tracking, enabling companies to stay up-to-date with regulatory changes and requirements.
Food safety training platform: Access to training materials and quizzes on demand to ensure workers have the necessary knowledge to operate following the latest food safety regulations, procedures, and best practices.
Temperature monitoring sensors: An IoT based solution that can be used to monitor temperature in freezers, refrigerators, and during transportation, sending alerts when temperatures fall outside of acceptable ranges. By using these sensors, companies can ensure that food is stored and transported at the appropriate temperature, reducing the risk of foodborne illness.
Remote monitoring devices: An Iot solution that monitors critical control points remotely, alerting staff of any deviations from critical limits in real-time. This tool will help companies reduce the risk of human error and improve food safety.
Smartphone-based solutions:
Mobile auditing and inspection apps: Enable staff to conduct audits and inspections from their mobile device, making it easier to collect data and ensure compliance.
The Hazard Analysis Critical Control Point (HACCP) system is an essential tool for ensuring the safety and quality of food products, it can minimize risks associated with foodborne illness and improve companies operational performance. The use of digital solutions can further enhance the effectiveness of the HACCP system by streamlining data collection, improving traceability, and providing real-time insights into the production and distribution process. Those tools will definitely help Canadian food and beverage companies ensure the safety and quality of their products while remaining competitive in an increasingly complex and dynamic market.
. . .

.jpg?width=400&name=shutterstock_1465552658%20(1).jpg)



